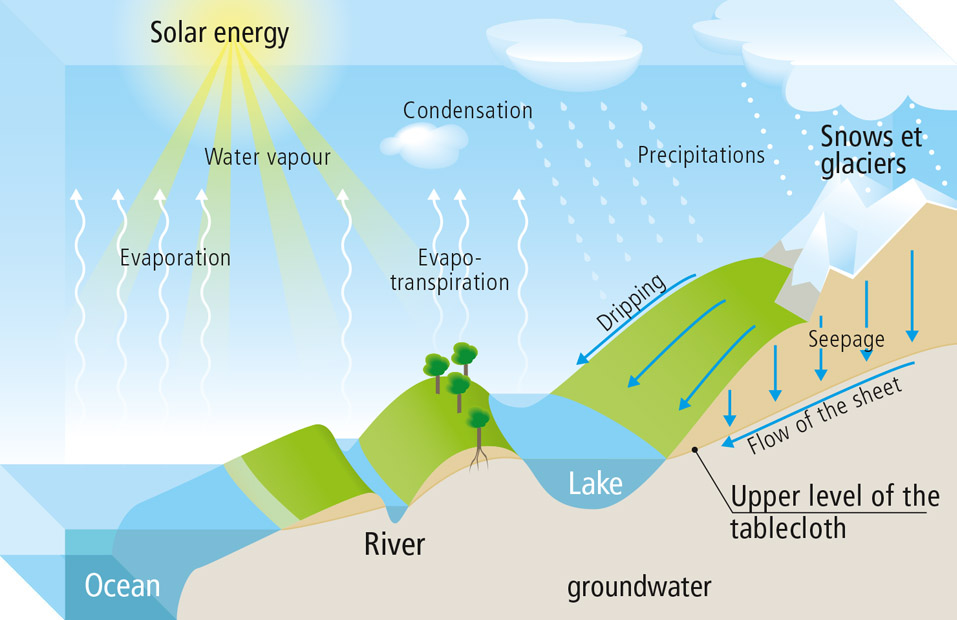
In nature, water actively participates in the life that exploits and transforms it. On a global scale, water is constantly passing through different states - liquid, water vapor, ice. This cycle resulting from the thermodynamics of our land ensures access to water for living beings and the recycling of materials and products that wastewater carries.
The growth of humans on earth would not have been possible without the increasingly sophisticated technologies of water transportation and treatment. These allow him to consume water and make the most of it while using the techniques of purifying rejected water in order to reintegrate it into the natural cycle.
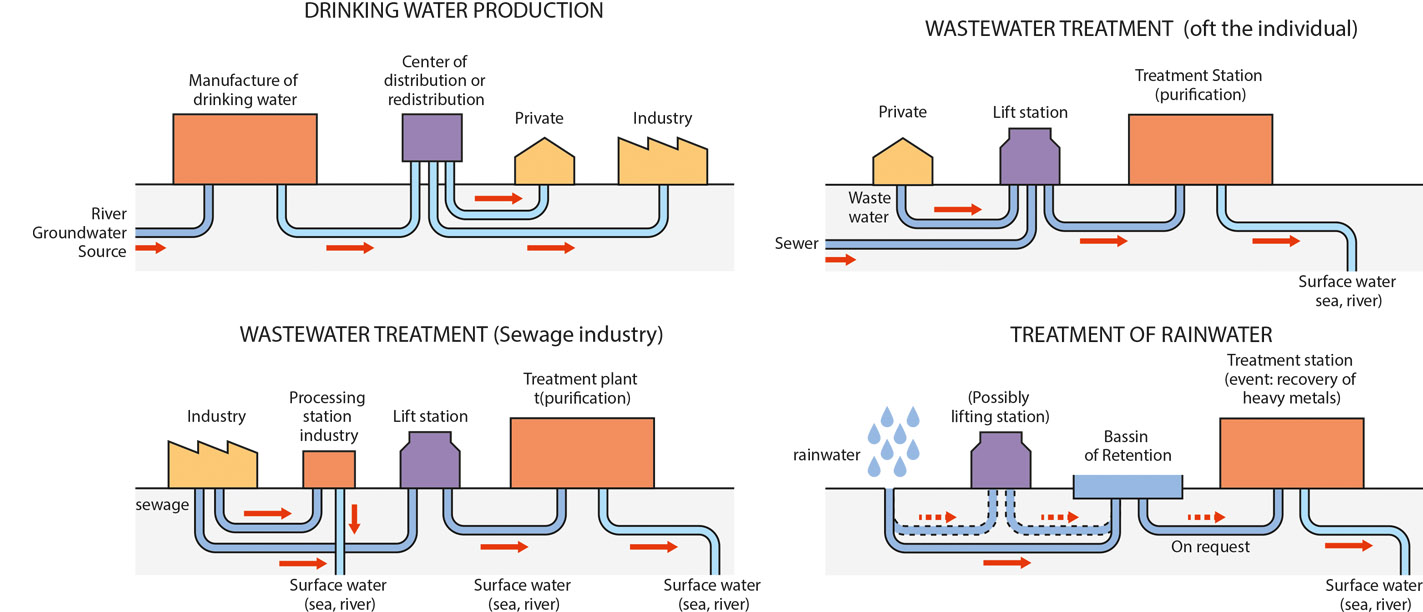
In parallel with the natural cycle, man treats water in various artificial cycles:
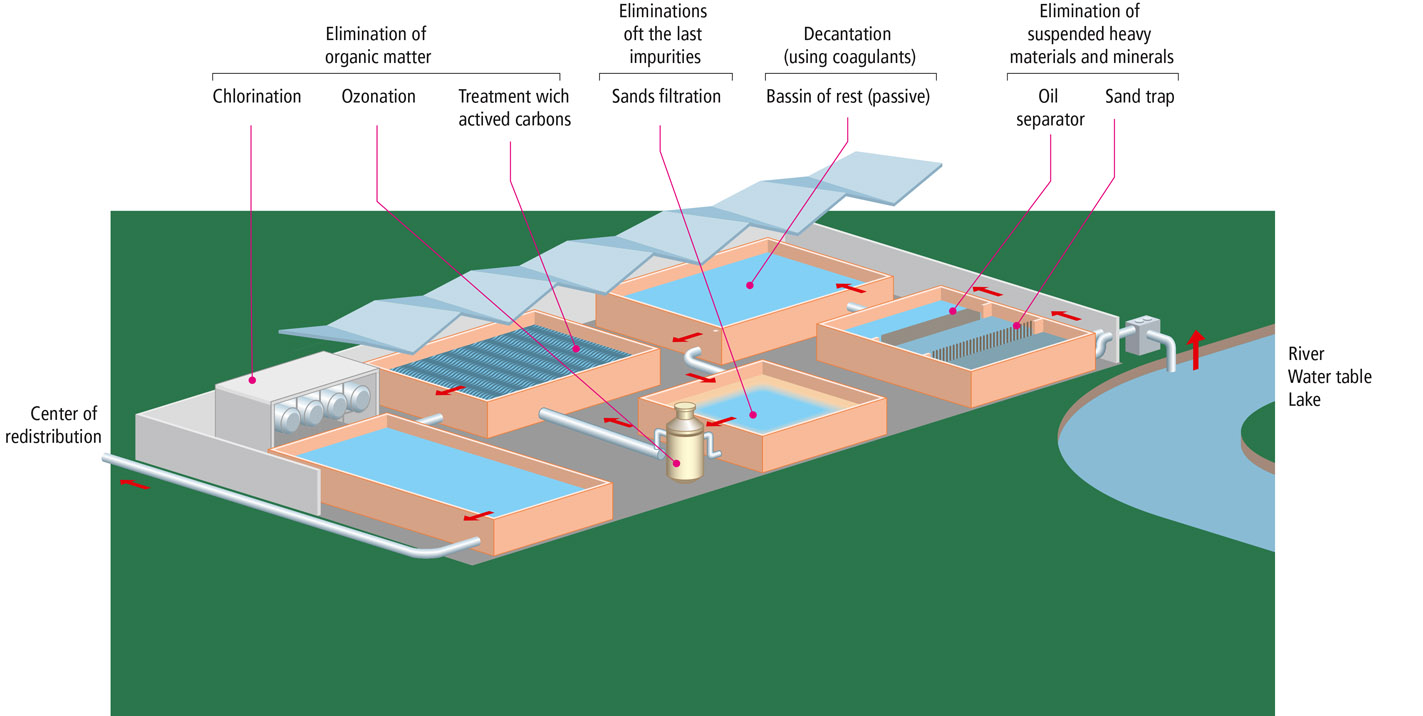
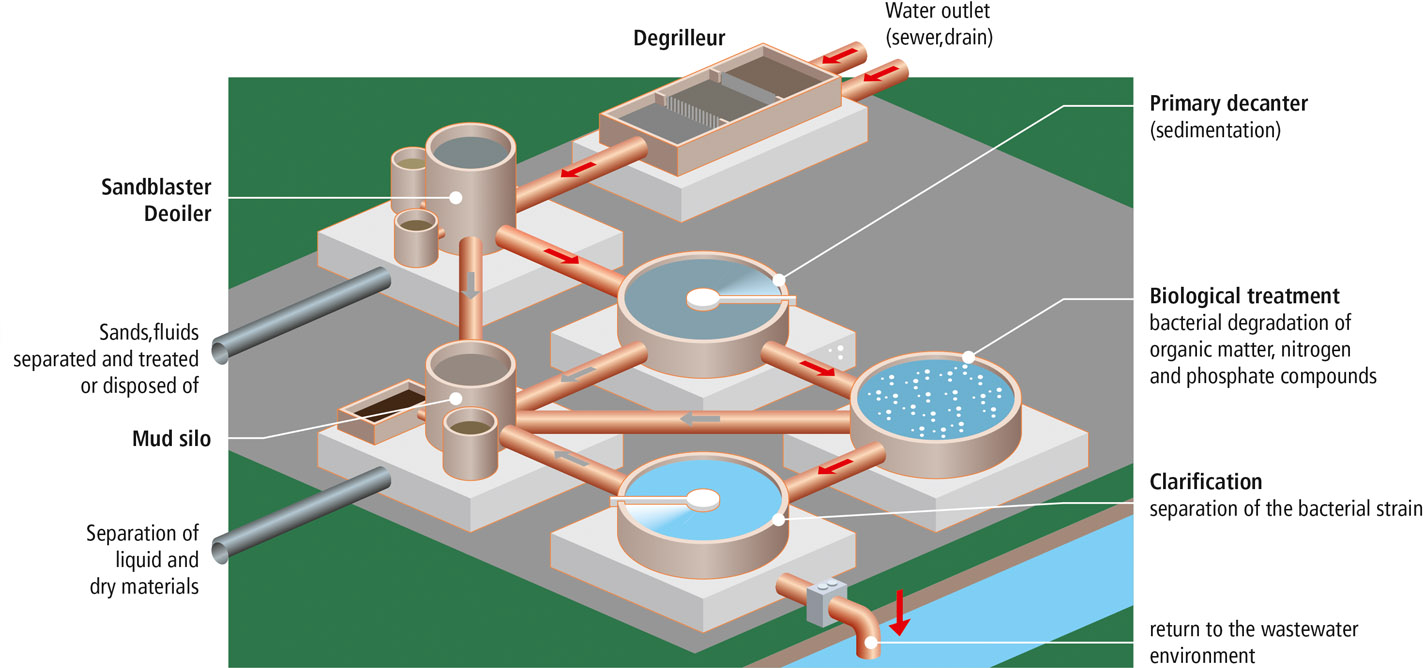
Mineral and organic impurities that are harmful to the health and use of man are separated from water of natural origin.
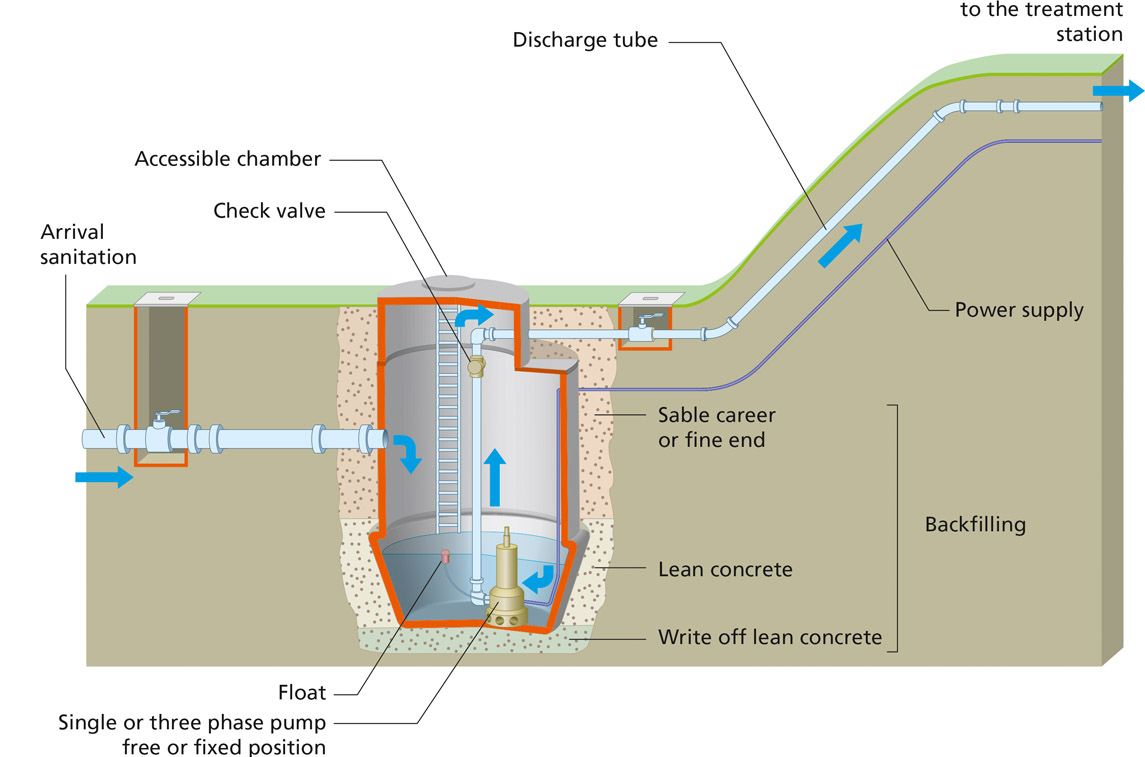
The lifting station ensures a further increase in pressure in case of occasional drop.
In use, the water is loaded with multitudes of impurities to be evacuated.
In order to minimize the pollution of nature, when a water laden with toxic products from industry and the private sector is discharged from the ground, it is passed to a treatment station which extracts and separates the foreign matter from its source. natural state.
These are mainly sludge separated by more or less passive treatments
The liquid must be transported from one point to another sometimes on long journeys. It must be routed without leaks between each of the stations, users and access to natural water. The range of components for the transport of water makes it possible to respond to all geological and topographical situations. What is this material made of?
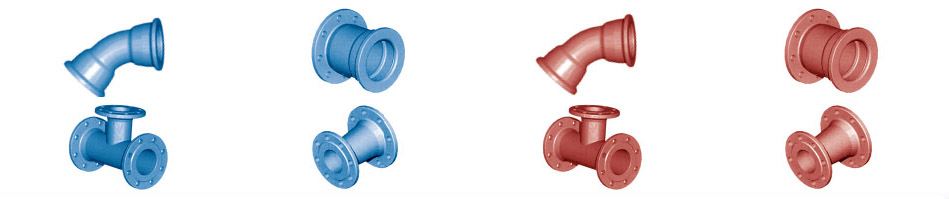
The use of the transported product is associated with the color of the equipment installed:
Depending on the use and the diameters requested different materials are available
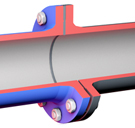
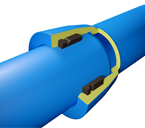
At high pressures (up to 100 Bar) the tulip connections are double chambered.
1. chamber: housing of the seal
2. room: housing of the keys of locking
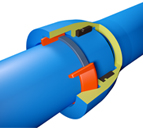
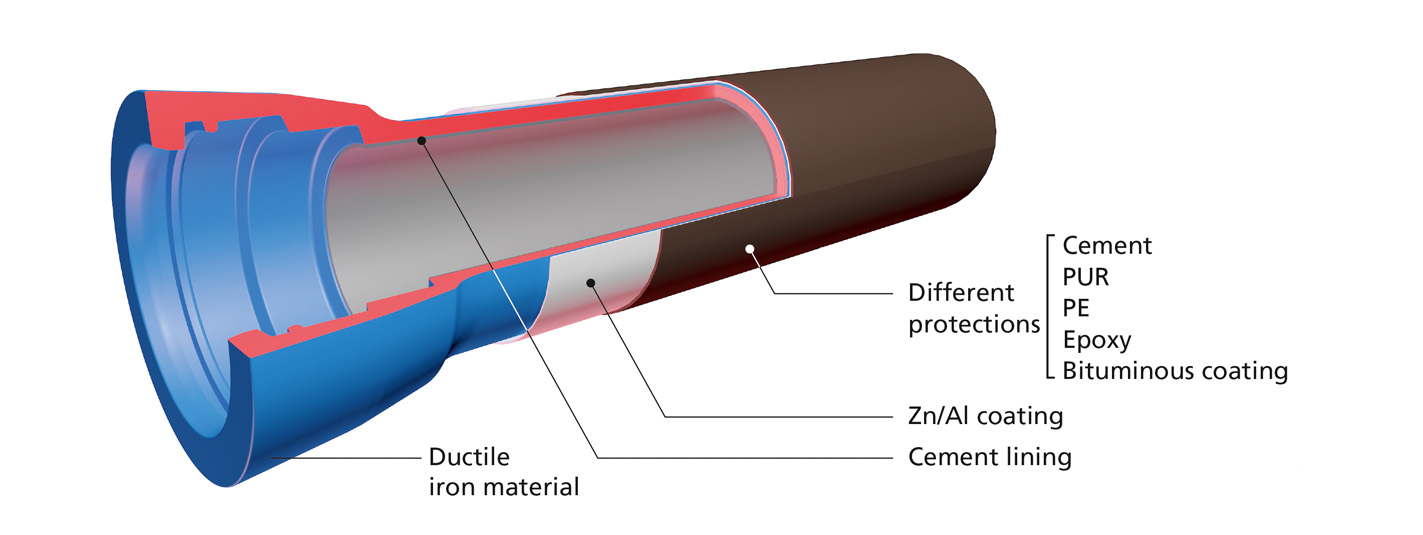
To avoid leaks many problems are to be solved. This "skin" that represents the walls of the pipes must be imperatively protected against the various mechanical, chemical or electrochemical attacks that can alter the substance of the inside as well as the outside.
Cement:
Active protection: As the cement is hygrophilic, it becomes impregnated with water and thus creates an alkaline environment protecting the melt from corrosion.
Passive protection: consists in producing a barrier between the cast iron and the transported liquid.
* To access pdf documents or for any other question, register or contact us directly.